Equilibrium Unemployment Theory Pissarides Pdf File
The unemployment story has many mansions, and this book owns one of them. It analyzes unemployment as a search-and-match-mediated equilibrium of flows through the labor market, set in motion by job destruction and job creation. The new edition adds endogenous job destruction and on-the-job search to the story, and can fairly claim to tell you everything you always wanted to know about search unemployment, but didn't know whom to ask.Robert M.
SolowInstitute Professor of Economics, emeritus, MIT. This book focuses on the modeling of the transitions in and out of unemployment, given the stochastic processes that break up jobs and lead to the formation of new jobs, and on the implications of this approach for macroeconomic equilibrium and for the efficiency of the labor market.An equilibrium theory of unemployment assumes that firms and workers maximize their payoffs under rational expectations and that wages are determined to exploit the private gains from trade. This book focuses on the modeling of the transitions in and out of unemployment, given the stochastic processes that break up jobs and lead to the formation of new jobs, and on the implications of this approach for macroeconomic equilibrium and for the efficiency of the labor market. This approach to labor market equilibrium and unemployment has been successful in explaining the determinants of the 'natural' rate of unemployment and new data on job and worker flows, in modeling the labor market in equilibrium business cycle and growth models, and in analyzing welfare policy.
Equilibrium Unemployment Theory Pissarides Pdf Files
The second edition contains two new chapters, one on endogenous job destruction and one on search on the job and job-to-job quitting. The rest of the book has been extensively rewritten and, in several cases, simplified.

Endorsements.The unemployment story has many mansions, and this book owns one of them. It analyzes unemployment as a search-and-match-mediated equilibrium of flows through the labor market, set in motion by job destruction and job creation. The new edition adds endogenous job destruction and on-the-job search to the story, and can fairly claim to tell you everything you always wanted to know about search unemployment, but didn't know whom to ask.Robert M. SolowInstitute Professor of Economics, emeritus, MIT.Pissarides incorporates imoprtant new developments into equilibrium unemployment theory. A particularly important development is endogenizing job destruction as well as job creation into a unified theoretical framework.
This framework, along with new data on job and worker flows, promises to provide a better understanding of unemployment.Edward C. PrescottUniversities of Chicago and Minnesota.Pissarides provides the labor-market building blocks for the new macroeconomics. A must read for everyone in macro and labor.Bob HallHoover Institution, Stanford University.Christopher Pissarides provides a definitive introduction to the search model of the labor market. The revised model, in dispensing with money and deriving real interest rates from real considerations, reveals itself to be a full subscriber to the natural-rate theory of unemployment. Among the several additions, the new chapter endogenizing job destruction is particularly valuable.Edmund PhelpsMcVickar Professor of Political Economy, Columbia University.
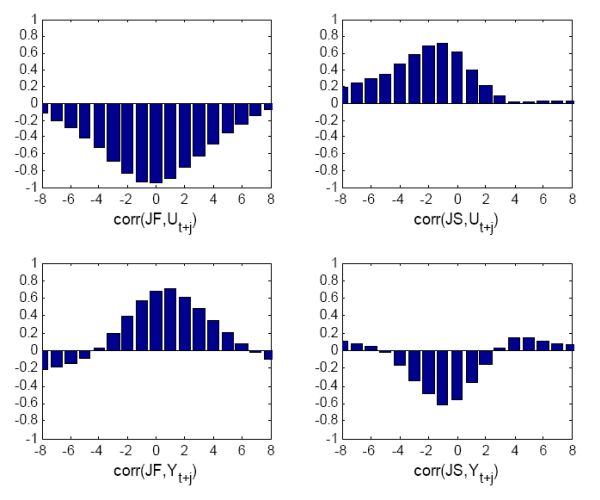
. 145 Downloads.AbstractThis paper presents a non-equilibrium, agent-based model of workers and firms, with on-the-job searching, endogenous entrepreneurial decisions and endogenous wage and income determination. Workers and firms are heterogeneous, and learn their strategy in the labor market. The model is able to reproduce a number of stylized facts generally accepted in labor economics and industrial organization, such as the Wage, Beveridge and Okun curve, and the skewness of wage, income and firm size distribution. Most interestingly, important stylized facts such as a negatively sloped Wage Curve and a constant returns to scale matching function emerge only out-of-equilibrium, during the adjustment processes toward the stationary state. Thus, from a theoretical point of view the model suggests that taking these stylized facts as “building blocks” of equilibrium models might be misleading. The results stress two additional points.
From a methodological point of view, the use of non-equilibrium computational models allows for a more comprehensive investigation of the labor market, by considering the endogenous character of many relevant variables. From an empirical point of view, the joint determination of all aggregate relationships and their dependence on the equilibrium or non-equilibrium state of the system suggest to move from the investigation of empirical regularities in isolation one from the other to a joint analysis.